气体净化及分离技术
术语和要点:Terminology&Key points
1. 基本概念 General:
1) 处理介质Processing medium:
• 压缩空气compressed air: 绝对压力大于0.1Mpa的空气
Air with absolute pressure greater than 0.1 Mpa
• 压缩气体:compressed gas 绝对压力大于0.1Mpa的气体;通常处理的气体为二氧化碳,氢气
Gases with absolute pressure greater than 0.1 Mpa;typically processed include carbon dioxide, hydrogen gas, and various chemical industrial tail gases.
2) 吸附adsorption:
• 气体、蒸汽或液体分子附着在固体表面上的物理过程。
Physical process in which the molecules of a gas, vapor or liquid adhere to the surface of a solid。
• 典型吸附材料为活性氧化铝,分子筛及硅胶;应用时依据不同露点要求单独使用或配比使用。
Common adsorbents such as activated alumina, molecular sieves, and silica gel are selected for use either individually or in optimized ratios, depending on the target dew point in the system.
3) 干燥器DRYER:
• 通过减少水蒸气含量来降低压缩气体的绝对含水量从而使出口相对湿度小于100%的设备。
Device that lowers absolute moisture content of compressed air by reducing water vapor content and the exit relative humidity is lower than 100%。
• 在一定处理量和工作压力及入口温度条件下,以下为干燥器的主要性能指标。
Under specified conditions of processing capacity, operating pressure, and inlet temperature, the following are the key performance parameters of the dryer
•压差或压降Δp differential pressure & pressure drop:
在规定条件下,测得的某部件进气口与出气口的压力之差。
Difference between the high and low pressure sides of a resistance to flow.
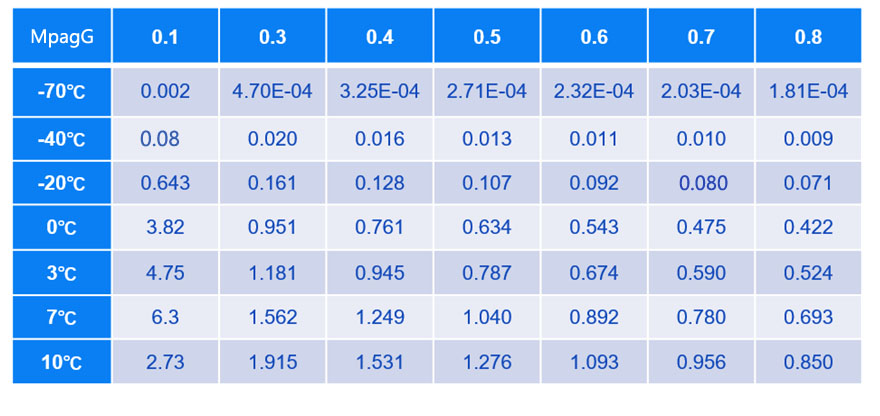
露点 dew point:
• 水蒸气开始凝结的温度。附表为不同压力下的不同露点的含水量表(g/kg):
The temperature at which water vapor begins to condense.Attached is a table of moisture content (g/kg) at different dew points under varying pressures
2. 压缩空气干燥器分类:Compressed air dryer classification:
吸附式干燥器adsorption dryer
借助于气相或液相水分子能吸附在吸附剂表面的原理分离出压缩空气中的水蒸气,并可通过各种方式除去吸附剂表面的水分而使吸附剂获得再生的干燥器。
The adsorption dryer operates on the principle that water molecules in either the gas or liquid phase adhere to the surface of an adsorbent, which effectively removes water vapor from compressed air or gas. Additionally, the dryer can regenerate the adsorbent by employing various methods to eliminate moisture from its surface, ensuring consistent and efficient drying performance.
2.1 无热再生吸附式干燥机(器) Heatless Regenerative(Desiccant)Dryer
•借助于未加热的、预先干燥过并减压膨胀的压缩空气流过吸附剂使吸附剂获得再生。
The adsorbent is regenerated by means of unheated, pre-dried and reduced-pressure expanded compressed air flowing through the desiccant.
2.2 有热再生吸附式干燥机(器)Heated Regenerative(Desiccant)Dryer
• 通过提高吸附剂的温度使其再生。
The desiccant is regenerated by increasing its temperature.
2.3 压缩热再生干燥机(器) Compression Heat Regenerative Dryer
• 利用压缩过程产生的、未经冷却的热压缩空气(有时需利用电加热辅助加热-入口温度低于110℃)来使吸附剂获得再生的一种吸附式干燥器。
An adsorption dryer that uses uncooled hot compressed air generated in the compression process (sometimes assisted by electric heating-inlet temperature below 110℃) to regenerate the desiccant.
2.4 鼓风热吸附式干燥机(器) Blower Regenerative (Desiccant)Drye
• 利用鼓风机将环境空气引入并通过加热器加热后对吸附剂进行加热再生的干燥器.
A dryer that uses a blower to introduce ambient air and heats it through a heater to heat and regenerate the desiccant.
2.5 零气耗压缩热再生干燥机(器)Zero purge Compression Heat Regenerative(Desiccant) Dryer
• 通过回收空压机排出的高温压缩空气的热量,直接加热吸附对吸附剂进行加热,加热完成后,利用原料气流经冷吹冷却器,对吸附剂进行冷吹。
The adsorbent is regenerated using heat recycled from the compressor's hot air, then cooled via process gas in a purge cooler.
2.6 零气耗鼓风热吸附式干燥机 Zero purge Blower Regenerative (Desiccant)Dryer
• 鼓风机将环境空气加压后,经加热器升温,用于加热吸附剂并脱附水分。再生完成后,利用环境空气鼓风气流经冷却器,对吸附剂进行冷吹降温,再生过程形成密闭循环系统,不消耗成品气体。
The blower pressurizes ambient air and heats it via a heater to regenerate the adsorbent by desorbing moisture12. After regeneration, the ambient airflow passes through a cooler to purge and cool the adsorbent, forming a closed-loop system with zero product gas consumption。
2.7 零气耗压缩热鼓风干燥机(器) Zero purge Heat of Compression & Blower Regenerative(Desiccant) Dryer
• 工作流程是一种结合压缩热回收技术与鼓风再生系统的吸附式干燥设备,其核心通过回收空压机末级排气余热或外加热源,对干燥剂进行加热,并利用鼓风机引入环境空气完成冷却,全程不消耗成品压缩空气,实现高效节能的压缩空气干燥。在需要达到低露点(-70℃)的工艺比零气耗鼓风干燥机降低能耗30%。
This adsorption dryer combines compressed heat recovery and blower regeneration, using compressor exhaust heat or external heat to regenerate desiccant. Ambient air from the blower cools the system without consuming product compressed air, enabling energy-efficient drying. For -70°C dew point applications, it reduces energy use by 30% vs. standard zero-purge dryers.
3. 干燥器工作过程和性能参数Dryer Working Process and Performance Parameters
1. 干燥剂 desiccant
有能力从压缩空气中去除水分的物质。
Substances having the ability to remove moisture from compressed air;
2. 活性氧化铝 activated alumina
具有从气体、蒸汽和一些液体中优先吸附水分能力的多孔颗粒型式的氧化铝。
Alumina of porous particle type with the ability to preferentially adsorb moisture from gases, vapors and some liquids.
3. 分子筛 molecular sieve
原子排列在一个晶格中从而有大量相互连接且孔径精确均匀的小孔的天然或合成材料。
A natural or synthetic material whose atoms are arranged in a crystal lattice so that there are a large number of interconnected pores with accurate and uniform pore sizes.
4. 再生气 regeneration air flow
通过非工作干燥介质的吹洗空气流。
purge air flow through the off-line drying media
5. 吹洗空气流 purge air flow
一股预干燥过的空气,用于脱除干燥介质上的湿气并带走水蒸气,也称为再生气。
A pre-dried air stream used to strip moisture from the drying medium and carry away water vapor, commonly referred to as regeneration air(gas).
6. 耗气量 consumption of purified compressed air
干燥器处理单位容积流量压缩空气所消耗的压缩空气量,以百分比来表示。
The amount of compressed air consumed by the dryer to process compressed air per unit volumetric flow, expressed as a percentage.
7. 零气耗 zero purge
干燥器处理单位容积流量压缩空气,再生过程中不消耗压缩空气成品气。
The dryer processes volume flow, and does not consume compressed air finished gas during the regeneration process.
8. 进气温度 Inlet Air Temperature
进入干燥器的压缩空气温度。当入口温度较高(例如超过40℃)时,湿负荷会显著增加(每升高5℃约增加30%),同时会降低吸附效率,导致出口露点温度每升高5℃就上升8-10℃
Temperature of compressed air entering the dryer. Higher inlet temperatures (e.g., above 40°C) significantly increase moisture load (~30% per 5°C rise) and degrade adsorption efficiency, raising outlet dew point by 8–10°C per 5°C increase
9. 入塔温度Adsorption Tower Inlet Temperature
特指压缩热干燥机在入塔吸附时的温度。这个温度基本等同于上述入口温度。同时这个温度由压缩热干燥机主冷却器的压缩空气出口温度。一般为冷却水入口温度增加6℃~8℃。
Specifically referring to the temperature of compressed heat dryers during the tower adsorption phase
This temperature is fundamentally equivalent to the inlet temperature mentioned earlier. It is governed by the compressed air outlet temperature of the main cooler in the compressed heat dryer system, typically ranging from 6°C to 8°C above the cooling water inlet temperature (ΔT = 6–8°C).
10. 处理量Processing Capacity
干燥机处理量指单位时间内可处理的压缩空气流量,通常以m3/min或Nm3/h(标准立方/米小时)表示。
Processing capacity refers to the compressed air flow rate that a dryer can handle per unit time, typically expressed inm³/min.
11. 工作压力Operating Pressure or working pressure:
在选择型号时应依系统的最低工作压力或压缩机出口的最低压力,据如下简易公式做修正,例如:
在入口温度一定时:
工作压力:0.55Mpa(g)
压缩机出口流量:100m³/min@0.7Mpa(g)
干燥机处理量=100*(0.1+0.7)/(0.1+0.55)≈123.0769min/min
Selection Principle
When selecting dryer models, the lowest system operating pressure or minimum compressor outlet pressure shall be used for correction. The simplified formula is:
Dryer Processing Capacity = Compressor Outlet Flow Rate × (Standard Pressure + Compressor Outlet Pressure) / (Standard Pressure + Minimum Operating Pressure)
Example Calculation
Given:
• Operating pressure (minimum): 0.55 MPa(g)
• Compressor outlet flow rate: 100 m³/min @ 0.7 MPa(g)
Calculation:
Dryer Processing Capacity=100×(0.1+0.7)/(0.1+0.55)≈123.08 m3/min
Key Notes
1. Standard Pressure: Typically defined as 0.1 MPa (atmospheric pressure reference).
2. Unit Consistency: All pressure values must use the same unit (e.g., MPa(g)).
3. Pressure Correction: This formula adjusts for reduced gas density at lower pressures to avoid dryer overload.
Terminology Clarification
• MPa(g): Megapascals (gauge pressure)
• Compressor outlet flow rate: Volumetric flow rate at compressor discharge conditions.
• Dryer processing capacity: Flow rate requirement after pressure correction .